So far 802.11 standard not mentioned any specific roam implementation until 802.11r amendment. So that each vendor will do the research in different ways and will come up with different solution. So we got different roaming techniques from diffrent vendors. But each roam technique have their own advantages and limitations. So 802.11r amendment came to standardize the roaming across different vendors and address all the existing limitations.
First we will understand the different available roam techniques and their limitations. Then we can go to 802.11r. Below are the different roam algorithms according to their priority from top to bottom.
CCKM : It is Cisco specific roam technique only. We can’t roam with other vendor infra.
MoveOp : It is Motorola specific roam technique only. We can’t roam with other vendor infra
Pre-auth : we need to pre-auth with many APs that will consume network resources. Each AP have to remember PMKSA of all the clients.
OKC : Each vendor Implemented on their own way. So inter vendor roaming and inter controller roaming not possible.
PMK Caching: We need to maintain PMK caching for each AP. Which is not possible when we have large networks.
802.11r advantages:
1. we can roam across different vendors using the standardized roam technique.
2. We should able to roam across entire ESS even APs may not be under same controller under same mobility domain.
3. We should able to reserve the required bandwidth at the time of connection it self.
4. Getting the AP neighbor reports .
5. We are able to roam less than 100 ms so that voice will continue without any breaks.
6. Authentication for the client device should be done only once.
FT definitions:
Mobility Domain : A set of BSS (basic service sets), within the same ESS (extended service set), that support Fast BSS transitions.
i.e All the APs under multiple controller will create one Mobility domain. So that client can roam between APs of different controller.
PMK-R0 : First level of the Fast BSS Transition key hierarchy. Derived from MSK (say PMK). Usually it is controller which will hold the PMK.
PMK-R1 : Second level of the Fast BSS Transition key hierarchy. Derived from PMK-R0.
Usually it is AP which will derive PMK-R1 keys.
FT Key Hierarchy:
FT Key Handling Process:
FT Methods:
Over-the-Air
• STA communicates directly with the target AP using FT authentication frames.
Over-the-DS
• STA communication to the target AP via current AP using FT Action frames.
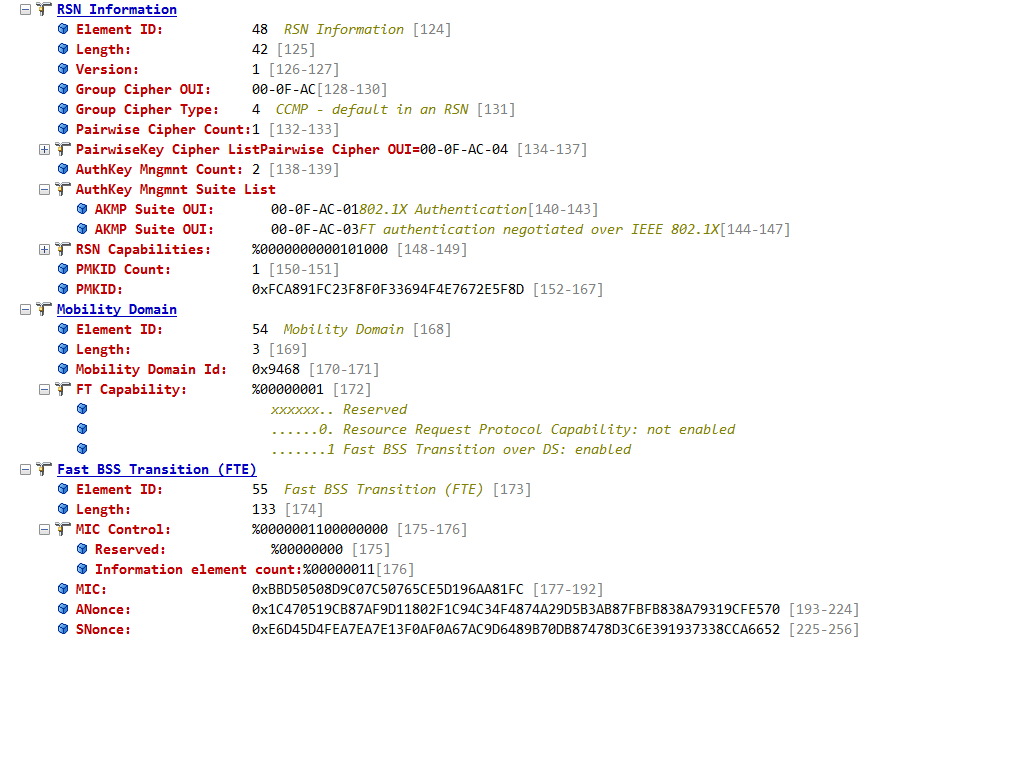
Below is the snapshot of beacon which specifies the FT Authentication as part of AKMP suite. We can see Mobility domain Filed and FT capability which tells it is using FT over Air or FT over DS.
FT Initial Association:
Below Capture will show us the FT Initial Association
Below packet shows the FT initial association request packet MDIE and RSNIE
Below packet shows the FT initial association response packet MDIE and FTIE
RSN Re-association (Over the Air):
Below capture shows the FT re-association procedure.
Below capture shows FT re-association request packet format
Below capture shows FT re-association response packet format